Cathodic protection glossary
Acid
Containing an excess of hydrogen ions over hydroxyl ions.
Alkaline
Containing an excess of hydroxyl ions over hydrogen ions.
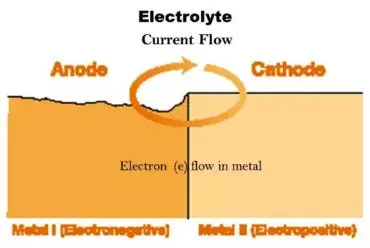
Anode
The electrode thru which direct cutting-edge enters an electrolyte.
Anodic area
The part of the steel surface that acts as an anode.
Bond
a chunk of metallic conductor, both strong or bendy, usually of copper, connecting two factors at the equal or on distinct structures, to prevent any considerable change inside the capacity of the only factor with respect to the alternative.
Calomel Reference Electrode
A reference electrode such as mercury and mercurous chloride (calomel) in a general answer of potassium chloride.
Carbonation
The chemical response between carbon dioxide and the calcium hydroxide present in Portland cement.
Cathode
The electrode through which direct modern leaves an electrolyte.
Cathodic area
The part of the steel surface that acts as a cathode.
Cathodic protection
a way of rendering a steel immune from corrosive assault with the aid of inflicting direct modern to glide from its electrolytic surroundings into the entire metal floor.
cell
A complete electrolytic device comprising of a cathode and an anode in electric touch with an intervening electrolyte.
Conductor
A substance (specially a steel or carbon) in which electric modern-day flows by using the movement of electrons.
Continuity Bond
A bond designed and set up especially to make sure the electric continuity of a shape.
Copper/Copper Sulphate Reference Electrode
A reference electrode which includes copper in a saturated copper sulphate answer.
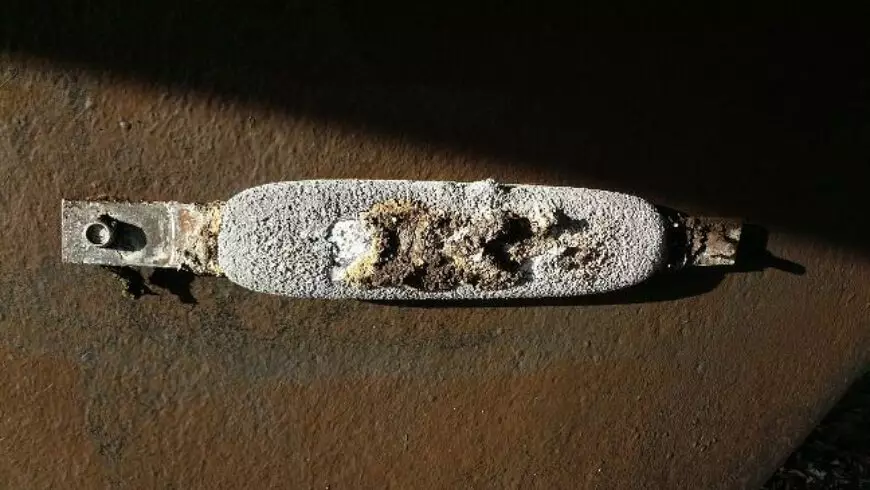
Corrosion
The chemical or electrochemical reaction of a metal with its surroundings, resulting in its revolutionary degradation or destruction.
Corrosion interaction
The boom or decrease inside the rate of corrosion, or tendency towards corrosion, of a buried or immersed structure resulting from the interception of part of the cathodic protection present day implemented to another shape or contemporary from other source.
current Density
The contemporary per unit geometrical region of the blanketed structure in contact with the electrolyte.
Electrode
A conductor of the metallic magnificence (which includes carbon) via which modern-day passes to or from an electrolyte.
Electrolyte
A liquid, or the liquid aspect in a composite material which includes soil, wherein the electrical modern-day flows by using motion of ions.
Electronegative
The nation of a metallic electrode whilst its capability is bad with appreciate to another metallic electrode in the gadget.
Electropositive
The country of a metal electrode whilst its ability is high quality with appreciate to some other metallic electrode inside the device.
Electrolyte
A liquid, or the liquid component in a composite fabric which includes soil, in which the electrical present day flows by using movement of ions.
Electro-osmosis
The passage of a liquid via a porous medium under the have an impact on of a potential difference.
Galvanic action
A spontaneous chemical response which occurs in a gadget comprising a cathode and an anode in electric contact and with an intervening electrolyte, resulting in corrosion of the anode.
Groundbed
A machine of buried or submerged electrodes related to the wonderful terminal of an independent source of direct modern-day, to be able to result in earth the current used for the cathodic safety of a buried or immersed metallic structure.
holiday
A defect in a protective coating at which metallic is uncovered.
Hydration (of cement)
The chemical and bodily reactions between cement and water from which the fabric derives its power.
Immunity
potential shifts on the monitoring reference cells being greater bad than -720 mV on interrupting the modern-day. this is the same old used for steel in seawater and is the cost at which corrosion is thermodynamically not possible because the anode reaction cannot be supported.
impressed current
The current provided by using a rectifier or different direct-cutting-edge supply (in particular aside from a sacrificial anode) to a blanketed shape if you want to obtain the essential safety capacity.
instantaneous-off potential
The shape/electrolyte potential measured immediately after the synchronous interruption of all sources of applied cathodic protection contemporary.
interaction take a look at
A check to decide the severity of corrosion interplay between buried or immersed structures.
Ion
An atom, or institution of atoms, carrying a effective or terrible electric price.
neutral
Containing same concentrations of hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions.
Passivity
The nation of the floor of a metallic or alloy vulnerable to corrosion where its electrochemical behavior becomes that of a less reactive steel and its corrosion price is reduced.
pH fee
A logarithmic index for the awareness of hydrogen ions in an electrolyte.
Pitting
A non-uniform corrosion of a metal whereby some of cavities, now not within the shape of cracks, are fashioned within the surface..
Polarization
alternate inside the capability of an electrode as the result of present day flow.
Polarization cell
A tool inserted within the earth connection of a shape that drains best a small cutting-edge from the supply used to provide cathodic safety for the shape, however presents a low resistance route to currents from high d.c. voltages and all a.c. voltages carried by using the structure.
primary structure
A buried or immersed shape cathodically covered by a device that could represent a supply of corrosion interaction with some other (secondary) structure.
protected shape
A structure to which cathodic protection is applied.
protection current
The contemporary made to circulate a metallic structure, with respect to a distinctive reference electrode in an electrolytic environment, needs to be depressed with the intention to effect cathodic safety of the shape.
protection capacity
The extra negative level to which the capability of a metallic shape, with respect to a specified reference electrode in an electrolytic surroundings, has to be depressed which will effect cathodic safety of the structure.
protective Coating
A dielectric cloth adhering to or bonded to a shape to separate it from its surroundings with a purpose to save you corrosion.
reaction (anodic, cathodic)
A method of chemical or electrochemical trade, specially taking vicinity at or close to an electrode in a cellular.
Redox potential
The capability taken up by a platinum electrode with recognize to a reference electrode.
Reference Electrode
An electrode the potential of that is appropriately reproducible and which serves as a basis of comparison in the measurement of other electrode potentials.
note: occasionally referred to as a ‘half of mobile’.
Saponification
The chemical method of forming a cleaning soap; more specifically a deterioration by softening of paint movies as a result of the motion of aqueous alkali on fatty-acid parts of the film.
Silver/Silver Chloride Reference Electrode
A reference electrode consisting of silver, coated with silver chloride, in an electrolyte containing chloride ions.
standard Hydrogen Electrode
A reference electrode such as an electro-high quality steel, which includes platinum, in an electrolyte containing hydrogen ions at unit pastime and saturated with hydrogen gasoline at 1 atm.
Stray current
cutting-edge flowing within the soil or water surroundings of a structure and bobbing up specially from cathodic safety, electric strength or traction installations, and that can bypass from the surroundings into the shape and vice versa.
Secondary structure
A buried or immersed shape that can be difficulty to corrosion interplay springing up from the cathodic safety of every other (the number one) shape.
structure/Electrolyte potential
The distinction in ability among a shape and a certain reference electrode in touch with the electrolyte at a point sufficiently close to (but without sincerely touching) the shape to keep away from errors due to the voltage drop related to any contemporary flowing within the electrolyte.
observe: comparable terms which include metal/electrolyte capacity, pipe/electrolyte potential, pipe/soil (water) potentials and so forth., as relevant in the precise context are used.
Unprotected structure
A shape to which cathodic protection is not carried out.
utilization factor
That proportion of anode fabric on an anode that can be ate up before the anode ceases to provide a modern output as required within the design.





No Comments